Medical Physics – The A To Z Of Allied Health
The discovery of x-ray in the 1890s led to the development of the medical physics group of professions.
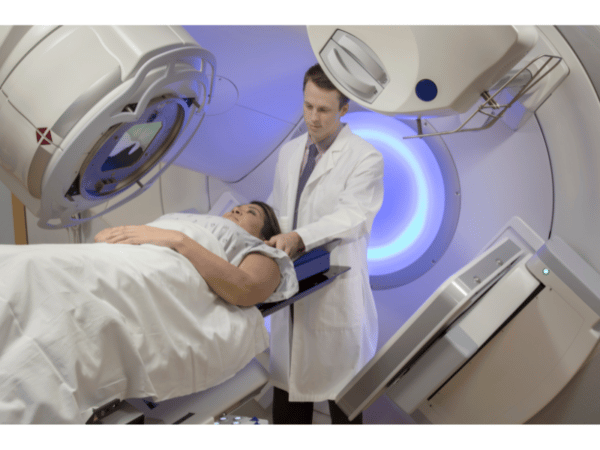
Medical physics is a diverse area of practice, with medical physicists typically engaging in a combination of clinical services and consultation, research, education, and training. Playing a critical role in the development and delivery of cancer treatments for an ageing population, the medical physicist profession is in high demand.
What does a medical physicist do?
This profession encompasses numerous sub-disciplines that include radiation oncology medical physics, the physics of radiological imaging, and nuclear medicine medical physics.
They will often be employed as part of a healthcare team and use their expertise in physics to develop and support the safe use of radiation, medical devices, and technology in the treatment of a range of health conditions.
Medical physicists may work with oncology doctors and teams to help determine the safest and most effective doses of radiation therapy. With their in-depth technical knowledge of imaging modalities and systems—including x-ray, ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, and ultraviolet light, and the technologies underpinning these—they also contribute to imaging teams.
Advantageous personal qualities and skills
Medical physicists rely on more than their deep knowledge of physics to do their job.
These professionals also need to have excellent problem-solving skills, teamwork and communication skills, as well as an in-depth working knowledge of information and general technology. Medical physics also involves developing and testing new technologies and techniques, so research capabilities come in very handy in this field of practice.
Where does a medical physicist work?
These professionals work in numerous countries including Australia, Canada, the USA, the UK, New Zealand, Hong Kong, and Singapore.
They usually work in hospitals in oncology settings, medical imaging, and nuclear medicine, in addition to working in non-hospital settings, including research institutions and with regulatory organisations.
Within the health setting, medical physicists fill a key advisory role to their team of professionals which, typically includes oncologists, radiologists, technologists, biomedical engineers, allied health professionals and safety advisers.
Medical physics professional education and regulatory frameworks
In many countries including Australia, aspiring medical physicists spend approximately five years studying. First, they need to complete an undergraduate science degree followed by a postgraduate master’s level qualification in medical physics. Medical physics students typically participate in workplace learning in a hospital or clinical environment.
Those in Canada must first attain an honours degree in physics, before undertaking graduate work in medical (or another area of) physics. From there, they complete a one- or two-year training program in medical physics.
To qualify as a medical physicist in the UK, the usual pathway is Bachelor of Healthcare Science degree, with Honours. Alternatively, those with a relevant degree can apply for a place on the NHS Scientist Training Programme, where a candidate trains as a clinical scientist specialising in medical physics.
In the USA, they undertake a combination of academic and workplace training, to attain a master’s or doctoral degree in medical physics.
To become a medical physicist in Hong Kong, students must complete a master’s degree in physics and receive a minimum of two years’ clinical training in a health workplace.
Regulatory Frameworks
In the UK, the this profession is regulated at the national level by the Health and Care Professions Council.
In Australia and New Zealand, it is self-regulated by the Australasian College of Physical Sciences and Engineers in Medicine.
Similarly, in Canada, it is self-regulated by The Canadian College of Physicists in Medicine.
In the USA, the individual states have regulations and licensure arrangements for medical physicists.
In Hong Kong, the profession is self-regulated via the Hong Kong Institute of Physicists in Medicine.
Medical physics workforce considerations
Medical physicists are critical to the development and delivery of treatments for cancer. With an ageing population and projections of increased cancer diagnoses, this profession is very much sought after.
Find out more about medical physics
- Step Into The NHS: Medical Physicists
- American Association of Physicists in Medicine
- Australasian College of Physical Scientists & Engineers in Medicine
- APEX Medical Physicists | New Zealand
- Canadian Organization of Medical Physicists
- Hong Kong Institution of Physicists in Medicine
- Society of Medical Physicists Singapore
If you have questions about the medical physics profession, or if you wish to share your experiences as a medical physicist, please leave a comment below.
Subscribe to Allied Health Insights to receive incisive and up-to-date allied health commentary and solutions. | Browse our range of insights into the allied health professions here.
If you offer professional development or business support services for medical physicists or their employers, please list your business on our Service Directory.
AHP Workforce provides allied health workforce planning, strategy and consulting for employers, managers and public sector stakeholders. For allied health workforce solutions, contact us today.